The gas strut, also called gas spring, gas pressure springs, gas dampers or gas pressure dampers, will solve your individual requirements for opening, closing, tilting and damping flaps, tables, seats or loungers thanks to our decades of experience. Gas struts take care of the controlled movement sequence and offer the following advantages:
The SUSPA standard product range of gas struts includes five different basic types 16-12, 16-1, 16-2, 16-4 and 16-6.
| Type | Ø Tube (mm) | Ø Piston rod (mm) | Stroke max. (mm) | Extension force F1 (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16-12 | 12 | 4 | 150 | 40 - 180 |
| 16-1 | 15 | 6 | 150 | 50 - 420 |
| 16-2 | 18.5 | 8 | 250 | 80 - 750 |
| 16-3 | 22 | 8 | 495 | 100 - 1,200 |
| 16-4 | 22 | 10 | 495 | 100 - 1,200 |
| 16-6 | 28 | 14 | 500 | 200 - 2,490 |
What is a gas strut? How is a gas strut built, how does it work and how do you find the right gas strut for your purpose? We will briefly present the most important functions here.
Gas struts are hydropneumatic adjustment elements.
Gas struts consist of a pressure tube and a piston rod with a piston unit. Connection parts to the pressure tube and the piston rod allow for the suitable connection for your application. The core of the SUSPA gas strut is the special sealing and guiding system. This ensures the hermetic sealing of the interior with low friction, even under extreme environmental conditions.
The gas strut is filled with non-toxic nitrogen under high pressure. This produces a charging pressure that acts on the cross-sectional area of the piston rod. This generates the extension force. If the extension force of the gas strut is higher than the force of the counterweight, the piston rod extends. If the extension force is lower, then the piston rod retracts. The flow cross-section in the damping system determines how quickly the extension occurs. In addition to nitrogen, there is a defined amount of oil in the interior for lubrication and end position damping. The suspension comfort of a gas strut can be determined as needed and for the respective task.
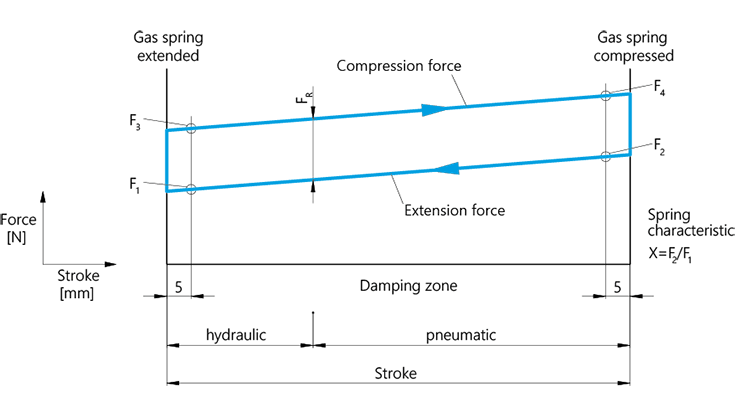
As can be seen from the graphic, the spring characteristic represents the force progression of the gas strut over the stroke, from the extended to the compressed state and back. In the process, the spring characteristic value represents the force ratio F2/F1. When designing a gas strut, the force F1 is the most important criterion in addition to the dimensions. The force F1 is measured 5 mm before the end of the extension movement, thus defining the value of the spring force. The force FR resulting from the friction is created between the force lines in the compressed and extension direction. The extension speed is divided into two types of damping: With the standard gas strut, the extension speed is controlled via a pneumatic and hydraulic range. When installing the gas strut with piston rod facing down, the piston first moves through the gas-filled part (pneumatic area), then through the oil-filled part of the pressure tube (hydraulic area). The piston rod is braked by the oil.
If desired, the damping can also occur dynamically. For this purpose, a longitudinal groove is provided in the pipe, which allows for a positionally-independent damping of the gas strut.
Gas struts with hydraulic damping can be designed as special versions according to the following principles:
The SUSPA gas struts Liftline are individually designed depending on the installation situation. For us, the focus is on the function of the entire application as well as the individual coordination of the kinematics and the spring characteristics in accordance with the requirements profile. Gas struts are tested in our technical department on systems, test equipment and trial facilities:
The following conditions are generally to be observed when selecting the suitable SUSPA gas strut:
SUSPA gas struts correspond to the highest requirements in a variety of application areas due to their basic design and their reliability. However, it is up to the user to check the suitability for the respective application case. We are happy to help you select the appropriate SUSPA gas strut and install it properly.